primes.rs
View source code here on GitHub!
Includes
- pub fn primes::primes<I>() -> impl Iterator<Item = I>
A convenience method that returns an iterator over the prime numbers.
- pub fn primes::primes_until<I>(x: I) -> impl Iterator<Item = I>
A convenience method that returns an iterator over the prime numbers until a given limit.
- pub struct primes::Eratosthenes<I> where I: Hash
This class implements the Sieve of Eratosthenes. In general, it will iterate over all of the prime numbers. You can also provide an optional
limitargument, which will force it to not yield any numbers above that limit. Below is a gif (courtesy of Wikipedia) that demonstrates the principle of the sieve.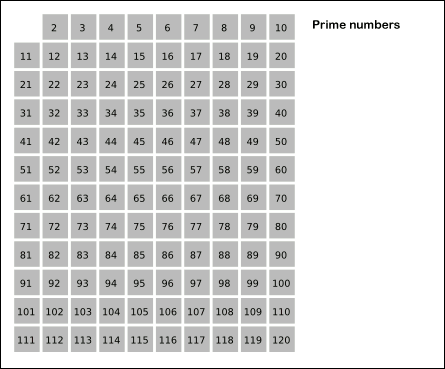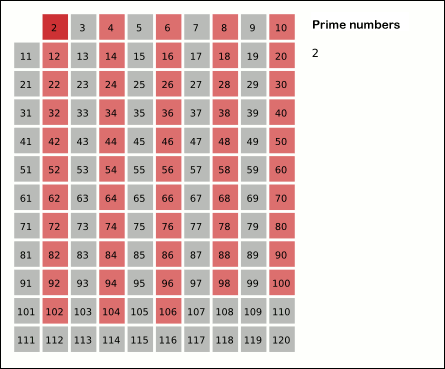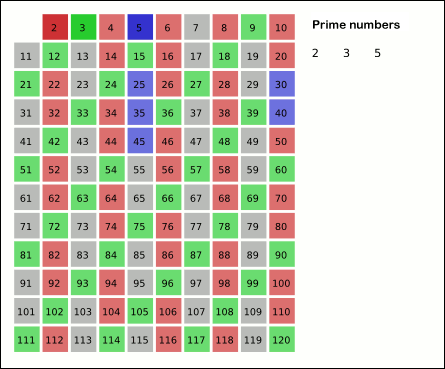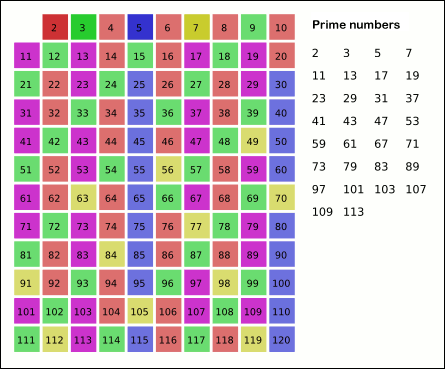
- pub fn primes::Eratosthenes::new() -> Eratosthenes<I> where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add
- pub fn primes::Eratosthenes::default() -> Eratosthenes<I> where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add
- pub fn primes::Eratosthenes::next() -> Option<I> where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add + Mul + Ord + Copy
- pub fn primes::prime_factors<I>(x: I) -> PrimeFactors<I>
A convenience method that returns an iterator over the prime factors of a given number.
- pub struct primes::PrimeFactors<I>
This class will iterate over all the prime factors of a number. It only supports positive integers. To find the factors of a negative number, iterate over the prime factors of its absolute value and add
-1as a factor manually.- pub fn primes::PrimeFactors::new(where I: NumAssign + Bounded + PartialOrd + Eq + Hash + Copyx: I)
- pub fn primes::PrimeFactors::next() -> Option<I> where I: Hash + Zero + One + Add + Ord + Copy + Div<Output=I> + Rem<Output=I>
- pub fn is_composite<I>(x: I) -> I where I: Hash + Zero + One + Add + Ord + Copy + Div<Output=I> + Rem<Output=I>
Returns
0if the number is prime, and the smallest prime factor otherwise.
- pub fn is_prime<I>(x: I) -> bool where I: Hash + Zero + One + Add + Ord + Copy + Div<Output=I> + Rem<Output=I>
Returns
trueif the number is prime, andfalseotherwise.
1use std::cmp::Ord;
2use std::collections::HashMap;
3use std::hash::Hash;
4use std::ops::{Add,Div,Mul,Rem};
5
6use num_traits::{one,zero,One,Zero};
7
8use crate::include::iter_cache::cache_iterator;
9
10#[derive(Clone, Debug)]
11pub struct Eratosthenes<I> where I: Hash {
12 sieve: HashMap<I, Vec<I>>,
13 prime: I,
14 candidate: I,
15}
16
17impl<I> Default for Eratosthenes<I> where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add {
18 fn default() -> Self {
19 return Eratosthenes::<I>{
20 sieve: HashMap::new(),
21 prime: zero::<I>(),
22 candidate: one::<I>() + one(),
23 };
24 }
25}
26
27impl<I> Eratosthenes<I> where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add {
28 pub fn new() -> Eratosthenes<I> {
29 return Default::default();
30 }
31}
32
33impl<I> Iterator for Eratosthenes<I> where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add + Mul + Ord + Copy {
34 type Item = I;
35
36 fn next(&mut self) -> Option<Self::Item> {
37 fn next_prime<I>(sieve: &mut HashMap<I, Vec<I>>, candidate: I) -> I
38 where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add + Mul + Ord + Copy
39 {
40 match sieve.get(&candidate) {
41 Some(numbers) => {
42 for num in numbers.to_owned() {
43 sieve
44 .entry(candidate + num)
45 .and_modify(|v| v.push(num))
46 .or_insert_with(|| vec![num]);
47 }
48 sieve.remove(&candidate);
49 return next_prime(sieve, candidate + one::<I>());
50 }
51 None => {
52 sieve.insert(candidate * candidate, vec![candidate]);
53 return candidate;
54 }
55 }
56 }
57
58 self.prime = next_prime::<I>(&mut self.sieve, self.candidate);
59 self.candidate = self.prime + one();
60 return Some(self.prime);
61 }
62}
63
64pub fn primes<I>() -> impl Iterator<Item = I> where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add + Mul + Ord + Copy + Send + 'static {
65 return cache_iterator(Eratosthenes::new());
66}
67
68pub fn primes_until<I>(x: I) -> impl Iterator<Item = I>
69where I: Hash + One + Zero + Add + Mul + Ord + Copy + Send + 'static
70{
71 return primes::<I>().take_while(move |n| *n < x);
72}
73
74#[derive(Clone, Copy, Debug, Hash)]
75pub struct PrimeFactors<I> {
76 number: I
77}
78
79impl<I> PrimeFactors<I> {
80 pub fn new(x: I) -> PrimeFactors<I> {
81 return PrimeFactors{
82 number: x
83 };
84 }
85}
86
87impl<I> Iterator for PrimeFactors<I>
88where I: Hash + Zero + One + Add + Ord + Copy + Div<Output=I> + Rem<Output=I> + Send + 'static
89{
90 type Item = I;
91
92 fn next(&mut self) -> Option<Self::Item> {
93 for p in primes() {
94 if self.number % p == zero() {
95 self.number = self.number / p;
96 return Some(p);
97 }
98 else if self.number < p {
99 break;
100 }
101 }
102 return None;
103 }
104}
105
106pub fn prime_factors<I>(x: I) -> impl Iterator<Item = I>
107where I: Hash + Zero + One + Add + Ord + Copy + Div<Output=I> + Rem<Output=I> + Send + 'static
108{
109 return PrimeFactors::new(x);
110}
111
112pub fn is_composite<I>(x: I) -> I
113where I: Hash + Zero + One + Add + Ord + Copy + Div<Output=I> + Rem<Output=I> + Send + 'static
114{
115 match prime_factors(x).next() {
116 None => {
117 return zero();
118 }
119 Some(number) => {
120 if number == x {
121 return zero();
122 }
123 return number;
124 }
125 }
126}
127
128pub fn is_prime<I>(x: I) -> bool
129where I: Hash + Zero + One + Add + Ord + Copy + Div<Output=I> + Rem<Output=I> + Send + 'static
130{
131 let two = one::<I>() + one::<I>();
132 if x < two {
133 return false;
134 }
135 let three = two + one();
136 if x <= three {
137 return true;
138 }
139 let five = (two * two) + one();
140 let six = (two + one()) * two;
141 let check = x % six;
142 return (check == one() || check == five) && is_composite(x) == zero();
143}