primes.js
View source code here on GitHub!
- primes.primes(stop=null)
Iterates over the prime numbers up to an (optional) limit, with caching.
This iterator leverages the
primes.modifiedEratosthenes()iterator, but adds additional features. The biggest is astopargument, which will prevent it from yielding any numbers larger than that. The next is caching of any yielded prime numbers.- Arguments:
stop (number|null)
- primes.modifiedEratosthenes()
Iterates over prime numbers using the Sieve of Eratosthenes.
This function implements the Sieve of Eratosthenes. In general, it will iterate over all of the prime numbers. Below is a gif (courtesy of Wikipedia) that demonstrates the principle of the sieve.
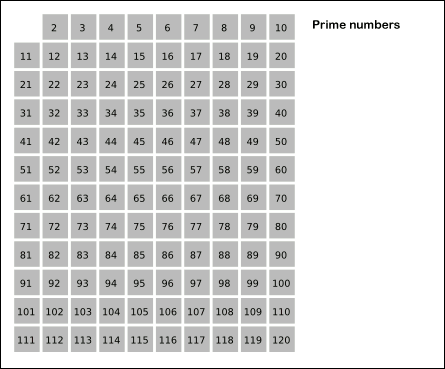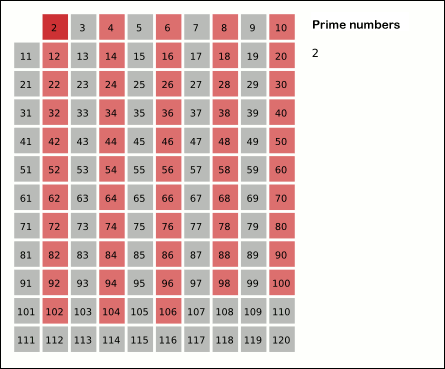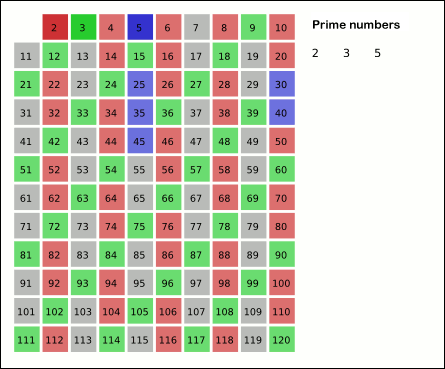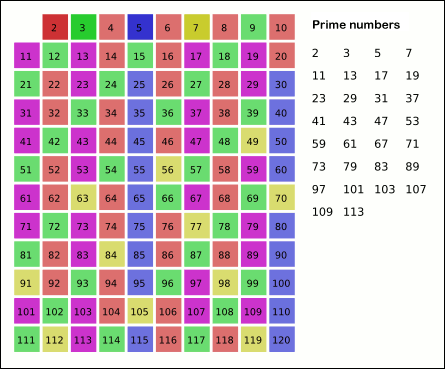
- primes.primeFactors(num)
Iterates over the prime factors of a number.
- Arguments:
num (number)
- primes.primesAndNegatives(stop=null)
Iterates over the prime numbers (and their negatives) up to an (optional) limit, with caching.
This iterator leverages the
primes.primes()iterator.- Arguments:
stop (number|null)
- primes.isComposite(n)
Tests if a number is composite
- Arguments:
n (number)
- Returns:
number -- 0 if prime, or the first prime factor if not
- primes.isPrime(n)
Tests if a number is prime
- Arguments:
n (number)
- Returns:
boolean --
1const cache = [2, 3, 5, 7];
2let lastCached = 7;
3
4/**
5 * Iterates over the prime numbers up to an (optional) limit, with caching.
6 *
7 * This iterator leverages the :js:func:`primes.modifiedEratosthenes` iterator, but adds
8 * additional features. The biggest is a ``stop`` argument, which will prevent it
9 * from yielding any numbers larger than that. The next is caching of any yielded
10 * prime numbers.
11 * @param {number | null} stop
12 * @yield {number}
13 */
14function* primes(stop = null) {
15 if (stop === null) {
16 for (const p of cache) {
17 yield p;
18 }
19 } else {
20 for (const p of cache) {
21 if (p < stop) {
22 yield p;
23 } else {
24 break;
25 }
26 }
27 }
28 if (stop !== null && lastCached > stop) {
29 return;
30 }
31 for (const p of modifiedEratosthenes()) {
32 if (p <= lastCached) {
33 continue;
34 }
35 if (stop !== null && p > stop) {
36 break;
37 }
38 cache.push(p);
39 lastCached = p;
40 yield p;
41 }
42}
43exports.primes = primes;
44
45
46/**
47 * Iterates over prime numbers using the Sieve of Eratosthenes.
48 *
49 * This function implements the `Sieve of Eratosthenes <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Eratosthenes>`_. In
50 * general, it will iterate over all of the prime numbers. Below is a gif (courtesy of Wikipedia) that demonstrates
51 * the principle of the sieve.
52 *
53 * .. image:: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/94/Animation_Sieve_of_Eratosth.gif
54 * :alt: Any animated example of the Sieve of Eratosthenes
55 * @yield {number}
56 */
57function* modifiedEratosthenes() {
58 yield 2;
59 yield 3;
60 yield 5;
61 yield 7;
62 const sieve = new Map();
63 const recurse = primes();
64 recurse.next();
65 let prime = recurse.next().value;
66 if (prime !== 3) {
67 throw new Error();
68 }
69 let primeSquared = prime * prime;
70 let step = 2;
71 for (let candidate = 9; ; candidate += 2) {
72 if (sieve.has(candidate)) { // if c is a multiple of some base prime, or
73 step = sieve.get(candidate);
74 sieve.delete(candidate);
75 } else if (candidate < primeSquared) { // prime, or
76 yield candidate;
77 continue;
78 } else { // the next base prime's square
79 // if candidate != primeSquared:
80 // raise ValueError()
81 step = prime * 2;
82 prime = recurse.next().value;
83 primeSquared = prime * prime;
84 }
85 let tc = candidate;
86 do {
87 tc += step; // the next multiple
88 } while (sieve.has(tc)); // make sure to not overwrite another sieve entry
89 sieve.set(tc, step);
90 }
91}
92exports.modifiedEratosthenes = modifiedEratosthenes;
93
94
95/**
96 * Iterates over the prime factors of a number.
97 *
98 * @param {number} num
99 * @yield {number}
100 */
101function* primeFactors(num) {
102 if (num < 0) {
103 yield -1;
104 num = -num;
105 }
106 if (num === 0) {
107 yield 0;
108 } else {
109 let root = Math.ceil(Math.sqrt(num));
110 for (const factor of primes()) {
111 let modulo = num % factor;
112 if (modulo == 0) {
113 while (modulo == 0) { // double-check to call sqrt once
114 yield factor;
115 num /= factor;
116 modulo = num % factor;
117 }
118 root = Math.ceil(Math.sqrt(num));
119 }
120 if (num <= 1) {
121 break;
122 }
123 if (factor > root) {
124 yield num;
125 break;
126 }
127 }
128 }
129}
130exports.primeFactors = primeFactors;
131
132/**
133 * Iterates over the prime numbers (and their negatives) up to an (optional) limit, with caching.
134 *
135 * This iterator leverages the :js:func:`primes.primes` iterator.
136 * @param {number | null} stop
137 * @yield {number}
138 */
139function* primesAndNegatives(stop = null) {
140 for (const p of primes(stop)) {
141 yield p;
142 yield -p;
143 }
144}
145exports.primesAndNegatives = primesAndNegatives;
146
147/**
148 * Tests if a number is composite
149 * @param {number} n
150 * @return {number} 0 if prime, or the first prime factor if not
151 */
152function isComposite(n) {
153 const factors = primeFactors(n);
154 const first = factors.next().value;
155 if (factors.next().done) {
156 return 0;
157 }
158 return first;
159}
160exports.isComposite = isComposite;
161
162/**
163 * Tests if a number is prime
164 * @param {number} n
165 * @return {boolean}
166 */
167function isPrime(n) {
168 if (n < 2) {
169 return false;
170 }
171 return !isComposite(n);
172}
173exports.isPrime = isPrime;